Idiopathic Osteoarthritis: 3 of 3 types of Osteoarthritis
Impact of Idiopathic Osteoarthritis on Joints
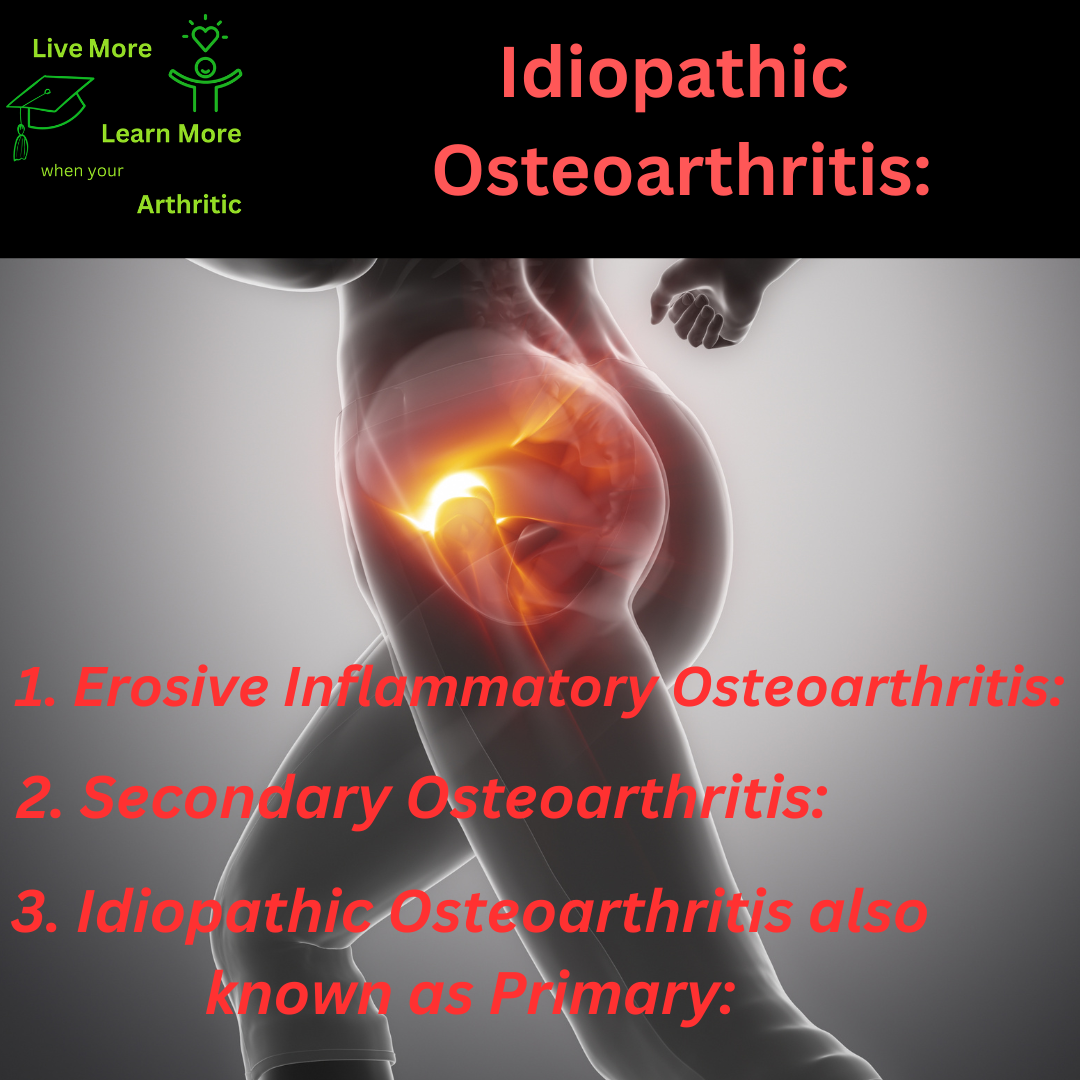
Idiopathic osteoarthritis, also known as primary osteoarthritis, predominantly affects certain joints in the body, with the following order of most to least affected:
- Knees: The knee joints are commonly affected by idiopathic osteoarthritis, often leading to pain and stiffness.
- Hips: Hip joints are frequently impacted, causing mobility issues and discomfort.
- Hands and Fingers: Joints in the hands and fingers may develop osteoarthritis, affecting dexterity and grip strength.
- Spine: Osteoarthritis can affect the spine, leading to back pain and reduced flexibility.
Here are the links to each remaining Osteoarthritis article covered in this 4 part series:
Disease Description
Idiopathic osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone changes. It typically develops without a known specific cause, hence the term “idiopathic.”
Causes and Triggers
The exact causes of idiopathic osteoarthritis are not fully understood but may involve a combination of genetic factors, aging, joint stress or injury, and biomechanical issues. Triggers can include repetitive joint use, obesity, and joint malalignment.
Symptoms and Limited Range of Motion
Common symptoms of idiopathic osteoarthritis include joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and decreased range of motion. Cartilage breakdown and bone spurs contribute to joint degeneration and functional impairment.
Age of Onset and Impact on Lifespan
Idiopathic osteoarthritis typically manifests in middle to older age, with the risk increasing with age. While it does not directly shorten lifespan, severe osteoarthritis can lead to mobility issues and reduced quality of life.
Autoimmune Nature and Risk Factors
Idiopathic osteoarthritis is not considered an autoimmune disease. Risk factors include advancing age, family history of osteoarthritis, joint injury, obesity, and certain occupations involving repetitive joint movements.
Complications and Inflammation
Inflammation in idiopathic osteoarthritis is primarily driven by local joint changes rather than systemic autoimmune responses. Joint swelling and inflammation can occur but are not as prominent as in inflammatory arthritis.
Joint Tenderness and Cartilage Loss
Tenderness in affected joints is common due to cartilage breakdown and bone changes. Over time, joint cartilage loss contributes to pain and stiffness, affecting joint function.
Impact on Range of Motion
Loss of range of motion in idiopathic osteoarthritis is attributed to joint damage, bone spurs, and soft tissue changes. Stiffness and pain worsen with joint use and can limit daily activities.
Achieving a Higher Quality of Life
A proactive approach can enhance quality of life with idiopathic osteoarthritis:
- Engage in low-impact exercises to strengthen muscles and maintain joint flexibility.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on joints.
- Use assistive devices or ergonomic aids to ease daily activities.
- Adopt joint-friendly lifestyle habits to minimize disease progression.
Possible Complications and Age Distribution
Complications of idiopathic osteoarthritis include joint deformities, chronic pain, reduced mobility, and impaired quality of life. It primarily affects older adults but can occur in younger individuals with risk factors.
Gender and Interconnected Conditions
Idiopathic osteoarthritis affects both men and women, with prevalence increasing in older age groups. Interconnected conditions may include osteoporosis, joint malalignment, and joint injuries, highlighting the importance of early intervention and holistic management.
Enjoy read 4 more articles about Osteoarthritis: